All engine lovers and enthusiasts agree that the sound of an internal combustion engine is a unique and characteristic melody of each vehicle. If the engine is the singer, the exhaust pipe of our motorcycle is the sound system that makes us perceive all the notes emanating from our engine.
In this article we are going to show you how to differentiate the different types of 4-stroke motorcycle exhausts so that you can choose the ideal one for yours and get the most out of it. Are you ready? Then put on your helmet and let's get started!
Parts of a motorcycle exhaust pipe
Before getting into the subject, it is important to know what are the parts of an exhaust pipe to know what role it occupies and if we are interested in replacing our complete exhaust, or only certain components of it.
Silencer: It is the final part of the exhaust. Its function is to reduce the sound generated by the engine and that is expelled by the exhaust pipe. At the same time it also acts as a beautifier and gives a sportier character to our motorcycles.
DB Killer: Component located at the exhaust manifold outlet that reduces the sound coming out of the muffler. It makes the sound waves return towards the interior of the silencer and decreases the decibels that finally reach us. To circulate without this element is punishable within the European Union.
Collector: Pipe of union between the exit orifice of the gases of the motor and the silencer. Depending on the material, the length of the manifold, diameter and shape, our motorcycle will acquire some characteristics or others.
Lambda sensor: This is a sensor that monitors the concentration of oxygen in the exhaust gases so that the engine can adjust the mixture of gasoline and air it sends.
Catalyzer: Element that filters and combines engine gases to reduce the polluting gases emitted to the exterior.
Types of exhaust pipes according to their installation
We can differentiate motorcycle exhausts by several criteria, one of them is according to how they are installed or mounted on our motorcycle. We can divide them into 2 types of exhausts: slip-on exhausts and full exhaust system.
Slip-On Exhausts
The slip-on exhausts only consist of an end silencer, adapters and a series of hooks and springs for fastening.

This type of exhausts are usually installed on the stock manifold of our bike by adjusting by means of a stainless steel or titanium elbow. As a general rule, we will have to cut our standard exhaust pipe to install the silencer and weld some hooks on the manifold so that by means of springs the exhaust is well adjusted if the elbow is not already installed. It is quite common that also incorporate a metal clamp to finish reinforcing the union and that it is well subject.
These motorcycle exhaust pipes have the advantage that they are cheaper than a complete exhaust system because we do not need to install new manifolds and we use the ones we already have on our motorcycle. In addition, we will gain sonority and we will reduce the weight by changing the standard silencer, which is usually more restrictive and heavy.
Full exhaust lines
Unlike Slip-On exhausts, complete exhaust lines incorporate all the necessary elements to replace the stock exhaust of your bike without modifying the original components.
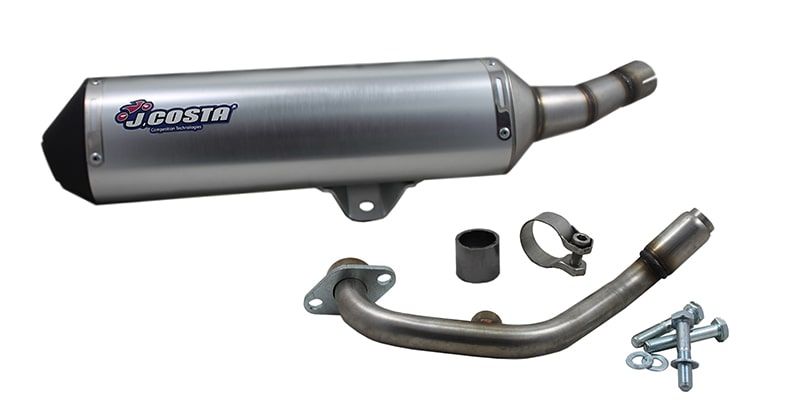

This type of exhaust provides us with higher performance, since they work with a tailor-made manifold, generally made of lighter materials than the standard manifolds. In addition, they provide the same advantages as a slip-on exhaust: the weight of the entire exhaust is reduced and a better sound is achieved.
The type of joint is usually cleaner than a Slip-On exhaust, since the manifold is designed to work in conjunction with the muffler. The fit is tighter and there is less chance of gas leakage.
On the other hand, complete exhaust lines are usually more expensive than if we buy only one silencer, although there are cheap complete exhausts for motorcycles that allow us to obtain performance without sacrificing price.
Exhaust types according to their homologation
When we talk about homologations we refer to the regulations established by the European Union, which are the most restrictive with respect to the rest of the countries in the world. We recommend that you consult the regulations established in your place of residence before choosing one exhaust system or another.
As established by the European Union, exhaust systems must meet a series of sound and emission standards to be considered homologated. Manufacturers must pass a series of inspections when launching a new exhaust model on the market in order to obtain the type-approval certificate for that product.
Driving with an unapproved exhaust pipe is not permitted and is punishable by a financial penalty and, in some cases, even the removal of the vehicle from the public road.
Within the homologated exhausts, we can distinguish 2 types of exhausts: catalyzed exhausts or non-catalyzed exhausts.
Uncatalyzed homologated exhaust pipes
The homologated exhaust pipes without a catalyzer are the most common to find in the market, since they comply with the regulations of sonority and specifications set by the Dirección General de Tráfico (DGT). This means that we can circulate with our exhaust without the risk of receiving a sanction.
The surprise and main difference is that, without the catalytic converter, the exhaust pipe does not retain the amount of gases that in many cases our motorcycle homologates. This means that it is likely that we will not pass the technical inspections (ITV) due to gas emissions.
So remember, don't get rid of your original exhaust until you are sure that your new exhaust meets the gas tests. Many users resort to their old exhaust to pass technical inspections.
Homologated catalyzed exhaust pipes
The catalytic converter is an element that acts as a filter inside our exhaust pipe, allowing only a percentage of the gases generated in our engine to escape to the outside. For this to happen, the catalytic converter combines the gases emitted by the engine to obtain a chemical compound that is not harmful, or at least not as harmful as if the gases were expelled without catalyzing.
Depending on the displacement of the motorcycle, the catalytic converter will be larger or smaller, even becoming unnoticeable because it is integrated directly into the manifold or silencer.
A homologated exhaust pipe with catalytic converter is the most comfortable and safe option to avoid worrying about gas emissions and not having to disassemble the exhaust every so often as mentioned above.
It's not all good news, since by installing a catalyzed exhaust we reduce to a certain extent the power we gain by changing our original pipe for another one and we will practically only get a better sound.
Catalyzed exhausts are the most difficult to find, as 90% of users prefer to install a non-catalyzed homologated exhaust pipe and save the cost of a catalyzed exhaust.
Conclusion
As in most cases, there is not one solution better than the other, but one type of exhaust pipe will be better for one type of user and other exhausts for others. What we do recommend is that if you want to change your exhaust pipe, install an approved exhaust to avoid problems with the law.
If you want to find a high quality and homologated exhaust with European certification, don't forget to visit our great selection of exhaust pipes for your motorcycle.

